ADULT EFFICACY


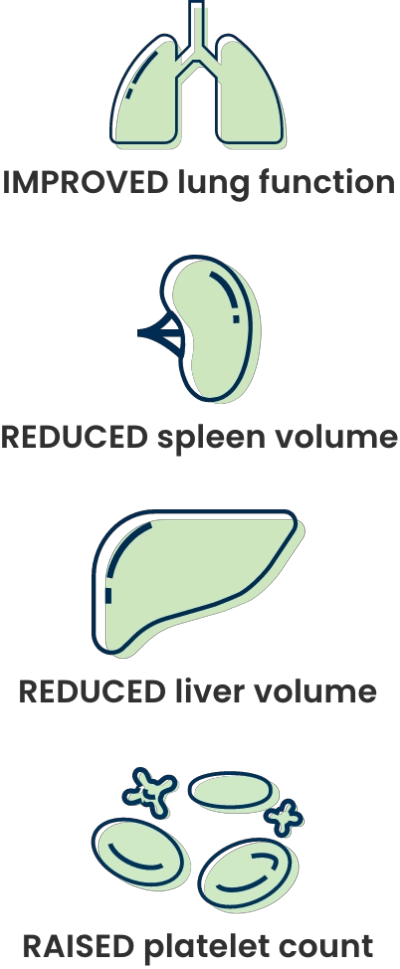
XENPOZYME achieved rapid, significant, and sustained improvements across key multisystemic signs and symptoms of ASMD1
Adult patients treated with XENPOZYME showed clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvements across multisystemic endpoints compared to placebo

In adult patients, XENPOZYME:

†First post-dose assessment.
XENPOZYME arm:
Baseline mean: 49.1% predicted
DLco;
Week 52 mean: 59.4% predicted
DLco
Placebo arm:
Baseline mean: 48.5% predicted
DLco;
Week 52 mean: 49.9% predicted
DLco.
Patients enrolled in the XENPOZYME arm during PAP experienced:
SUSTAINED 34% IMPROVEMENT in % predicted DLco at Week 104 (n=5) vs baseline (n=13)
XENPOZYME arm:
Baseline mean: 49.1% predicted
DLco;
Week 52 mean: 59.4% predicted
DLco
Placebo arm:
Baseline mean: 48.5% predicted
DLco;
Week 52 mean: 49.9% predicted
DLco.

†First post-dose assessment.
Patients enrolled in the XENPOZYME arm during PAP experienced:
SUSTAINED 48% REDUCTION in spleen volume (MN) at Week 104 (n=9) vs baseline (n=13)
XENPOZYME arm:
Baseline mean: 11.5 MN
Week 52 mean: 7.2 MN
Placebo arm:
Baseline mean: 11.2 MN
Week 52 mean: 11.2 MN

†First post-dose assessment.
Patients enrolled in the XENPOZYME arm during PAP experienced:
SUSTAINED 32% REDUCTION in liver volume (MN) at Week 104 (n=9) vs baseline (n=13)
XENPOZYME arm:
Baseline mean: 1.4 MN
Week 52 mean: 1.0 MN
Placebo arm:
Baseline mean: 1.6 MN
Week 52 mean: 1.6 MN

Patients enrolled in the XENPOZYME arm during PAP experienced:
SUSTAINED 24% INCREASE in platelet count (109/L) at Week 104 (n=9) vs baseline (n=13)
XENPOZYME arm:
Baseline mean: 109.3 × 109/L
Week 52 mean: 126.4 × 109/L
Placebo arm:
Baseline mean: 115.6 × 109/L
Week 52 mean: 120.2 × 109/L
Patients previously in the placebo arm who crossed over to XENPOZYME at Week 52 experienced multisystemic improvements at Week 104 from baseline1,2
Notable multisystemic improvements were observed in patients who crossed over from placebo to XENPOZYME at Week 52.

*Week 104 n values.
ASMD=acid sphingomyelinase deficiency; DLco=diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide; MN=multiples of normal; PAP=primary analysis period.
Learn more about XENPOZYME efficacy in pediatric patients.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
|
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS Patients treated with XENPOZYME have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment, should be readily available during XENPOZYME administration. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue XENPOZYME immediately, and initiate appropriate medical treatment. In patients with severe hypersensitivity reactions, a desensitization procedure to XENPOZYME may be considered. |
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
See Boxed WARNING. Prior to XENPOZYME administration, consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids.
- If a severe hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue XENPOZYME immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Consider the risks and benefits of re-administering XENPOZYME following severe hypersensitivity reactions.
- If a mild or moderate hypersensitivity reaction occurs, consider temporarily holding the infusion, slowing the infusion rate, and/or reducing the XENPOZYME dose.
Infusion-Associated Reactions
Antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids may be given prior to XENPOZYME administration to reduce the risk of infusion-associated reactions (IARs). However, IARs may still occur in patients after receiving pretreatment.
- If severe IARs occur, discontinue XENPOZYME immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Consider the risks and benefits of re-administering XENPOZYME following severe IARs.
- If a mild or moderate IAR occurs, the infusion rate may be slowed or temporarily withheld, and/or the XENPOZYME dosage may be reduced.
Acute phase reactions (APRs), acute inflammatory responses accompanied by elevations in inflammatory serum protein concentrations, have been observed. Most APRs occurred at 48 hours post infusion during the dose escalation period. APRs were managed similar to other IARs.
Elevated Transaminase Levels
XENPOZYME may be associated with elevated transaminases (ALT, AST, or both) within 24 to 48 hours after infusion. Levels generally returned to levels observed prior to the XENPOZYME infusion. To manage the risk of elevated transaminase levels, assess ALT and AST:
- within one month prior to initiation of XENPOZYME,
- within 72 hours prior to any infusion during dose escalation, which includes the first 3 mg/kg dose, or prior to the next scheduled XENPOZYME infusion upon resuming treatment following a missed dose.
Upon reaching the recommended maintenance dose, transaminase testing is recommended to be continued as part of routine clinical management of ASMD.
Risk of Fetal Malformations During Dosage Initiation or Escalation in Pregnancy
XENPOZYME dosage initiation or escalation, at any time during pregnancy, is not recommended as it may lead to elevated sphingomyelin metabolite levels that may increase the risk of fetal malformations. The decision to continue or discontinue XENPOZYME maintenance dosing in pregnancy should consider the female’s need for XENPOZYME, the potential drug-related risks to the fetus, and the potential adverse outcomes from untreated maternal ASMD disease.
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating XENPOZYME treatment. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during XENPOZYME treatment and for 14 days after the last dose if XENPOZYME is discontinued.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most frequently reported adverse drug reactions in adults (incidence ≥10%) were headache, cough, diarrhea, hypotension, and ocular hyperemia.
- Most frequently reported adverse drug reactions in pediatric patients (incidence ≥20%) were pyrexia, cough, diarrhea, rhinitis, abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, urticaria, nausea, rash, arthralgia, pruritus, fatigue, and pharyngitis.
INDICATION
XENPOZYME® (olipudase alfa-rpcp) is indicated for treatment of non–central nervous system manifestations of acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) in adult and pediatric patients.
Please see full Prescribing Information for complete details, including Boxed WARNING.
References: 1. XENPOZYME. Prescribing Information. 2. Data on file, Sanofi.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
|
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS Patients treated with XENPOZYME have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment, should be readily available during XENPOZYME administration. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue XENPOZYME immediately, and initiate appropriate medical treatment. In patients with severe hypersensitivity reactions, a desensitization procedure to XENPOZYME may be considered. |
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
See Boxed WARNING. Prior to XENPOZYME administration, consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids.
- If a severe hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue XENPOZYME immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Consider the risks and benefits of re-administering XENPOZYME following severe hypersensitivity reactions.
- If a mild or moderate hypersensitivity reaction occurs, consider temporarily holding the infusion, slowing the infusion rate, and/or reducing the XENPOZYME dose.
Infusion-Associated Reactions
Antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids may be given prior to XENPOZYME administration to reduce the risk of infusion-associated reactions (IARs). However, IARs may still occur in patients after receiving pretreatment.
- If severe IARs occur, discontinue XENPOZYME immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Consider the risks and benefits of re-administering XENPOZYME following severe IARs.
- If a mild or moderate IAR occurs, the infusion rate may be slowed or temporarily withheld, and/or the XENPOZYME dosage may be reduced.
Acute phase reactions (APRs), acute inflammatory responses accompanied by elevations in inflammatory serum protein concentrations, have been observed. Most APRs occurred at 48 hours post infusion during the dose escalation period. APRs were managed similar to other IARs.
Elevated Transaminase Levels
XENPOZYME may be associated with elevated transaminases (ALT, AST, or both) within 24 to 48 hours after infusion. Levels generally returned to levels observed prior to the XENPOZYME infusion. To manage the risk of elevated transaminase levels, assess ALT and AST:
- within one month prior to initiation of XENPOZYME,
- within 72 hours prior to any infusion during dose escalation, which includes the first 3 mg/kg dose, or prior to the next scheduled XENPOZYME infusion upon resuming treatment following a missed dose.
Upon reaching the recommended maintenance dose, transaminase testing is recommended to be continued as part of routine clinical management of ASMD.
Risk of Fetal Malformations During Dosage Initiation or Escalation in Pregnancy
XENPOZYME dosage initiation or escalation, at any time during pregnancy, is not recommended as it may lead to elevated sphingomyelin metabolite levels that may increase the risk of fetal malformations. The decision to continue or discontinue XENPOZYME maintenance dosing in pregnancy should consider the female’s need for XENPOZYME, the potential drug-related risks to the fetus, and the potential adverse outcomes from untreated maternal ASMD disease.
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating XENPOZYME treatment. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during XENPOZYME treatment and for 14 days after the last dose if XENPOZYME is discontinued.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most frequently reported adverse drug reactions in adults (incidence ≥10%) were headache, cough, diarrhea, hypotension, and ocular hyperemia.
- Most frequently reported adverse drug reactions in pediatric patients (incidence ≥20%) were pyrexia, cough, diarrhea, rhinitis, abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, urticaria, nausea, rash, arthralgia, pruritus, fatigue, and pharyngitis.
INDICATION
XENPOZYME® (olipudase alfa-rpcp) is indicated for treatment of non–central nervous system manifestations of acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) in adult and pediatric patients.
Please see full Prescribing Information for complete details, including Boxed WARNING.
References: 1. XENPOZYME. Prescribing Information. 2. Data on file, Sanofi.


